
TASECS – Turkish Aerospace Environmental Control Systems was established in 2019 as the only company in Türkiye specializing in the design and production of environmental control systems for military and civilian air platforms, with a focus on nationally developed and indigenous solutions. A wholly owned subsidiary of TUSAŞ – Turkish Aerospace Industries Inc., TASECS contributes to the localization efforts of the Turkish defense and aerospace industry by delivering high-tech environmental control systems that enhance the operational performance and mission readiness of airborne platforms.
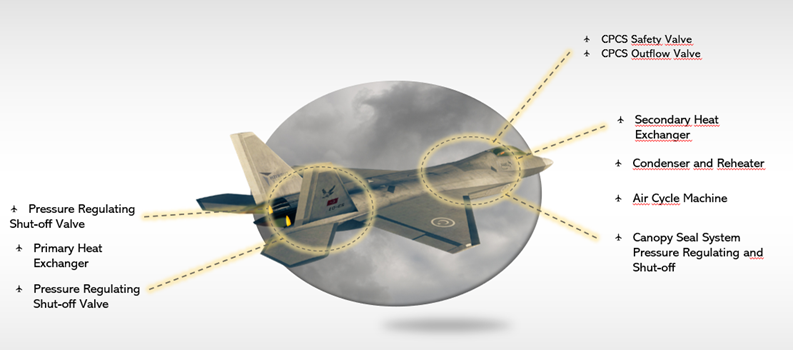
TASECS offers Air Cycle Cooling Systems (ACCS) designed for efficient cooling and pressurization across various aviation applications. These systems utilize air bled from the main engine compressor, which is expanded through a turbine. The turbine drives a compressor that compresses the air, initiating the cooling cycle. In this way, excess thermal energy is converted into useful work that powers the components of the cooling cycle.
Modulating valves control the flow of air or fluids within systems, adjusting to varying demands for precise control. These valves are designed to regulate pressure, temperature, and flow, optimizing performance in diverse conditions.

Check valves prevent reverse flow within systems, ensuring that the flow of air or fluid is unidirectional. These valves are crucial for preventing backflow, maintaining system pressure, and protecting components from damage.

Condensers facilitate heat transfer by condensing fluid in the vapor phase within systems. They are optimized to improve thermal efficiency and reduce energy consumption.

Evaporators are used to evaporate liquid fluids for cooling or heat removal purposes. They play a critical role in heat transfer.

TASECS offers advanced Vapor Cycle Cooling Systems (VCCS) designed to efficiently transfer heat from low-temperature environments to higher-temperature ones, similar to a heat pump. The vapor cycle system operates by absorbing heat from the source fluid as the liquid refrigerant evaporates in the evaporator. The refrigerant is then compressed to a higher pressure and temperature, after which it is cooled in the condenser, releasing the absorbed heat to the heat sink. The refrigerant liquid leaving the condenser flows to the evaporator through an expansion valve, completing the closed-loop cycle.
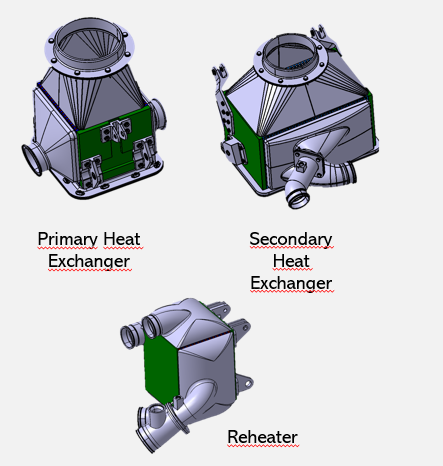
Primary and secondary heat exchangers transfer heat between different fluid circuits to increase the system’s energy conversion efficiency.
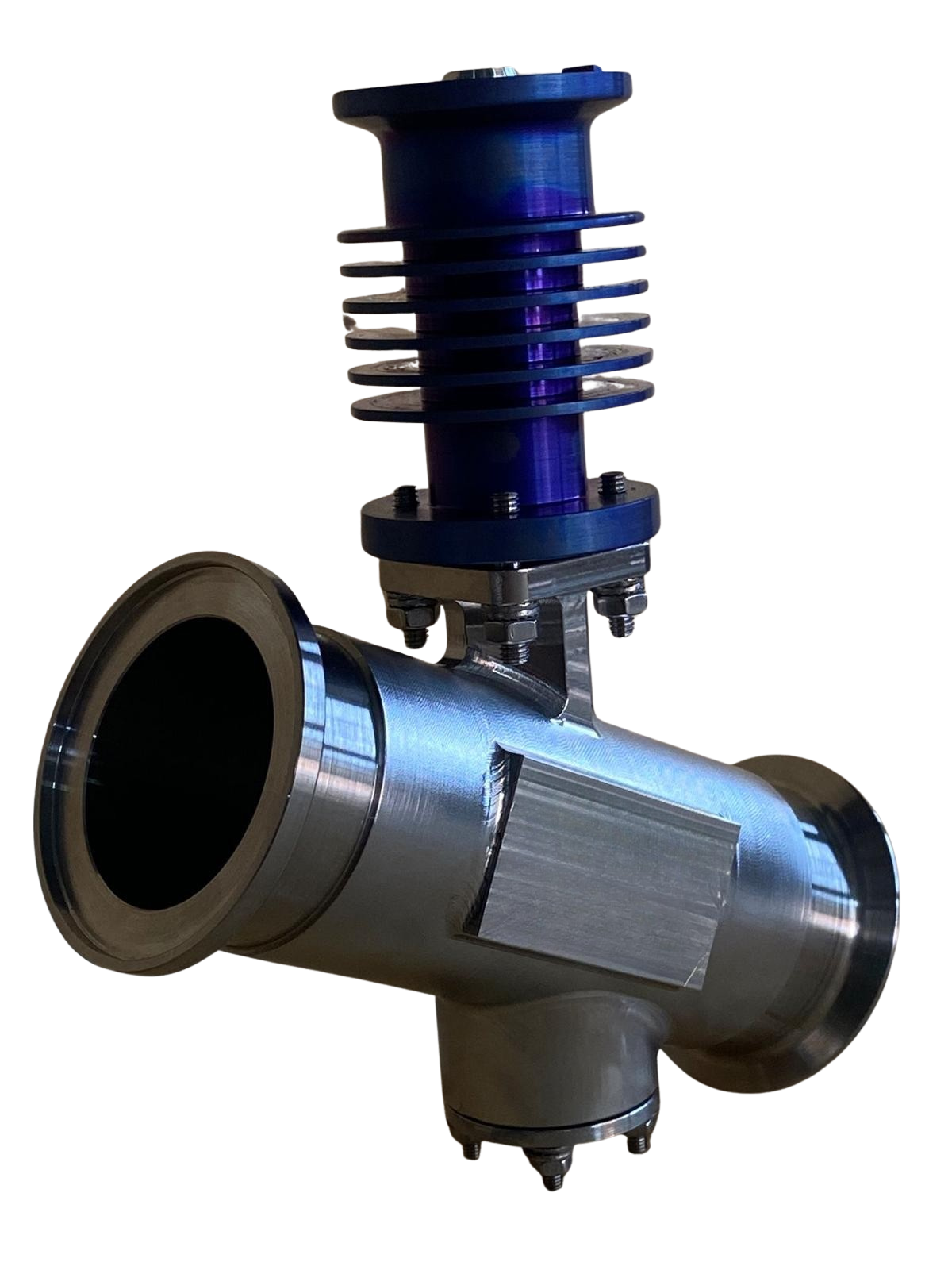

Shut-off valves provide a critical function by completely stopping or allowing the flow of air or fluids in a system. These valves are essential for ensuring safety and system integrity, with fast and reliable operation under all conditions.
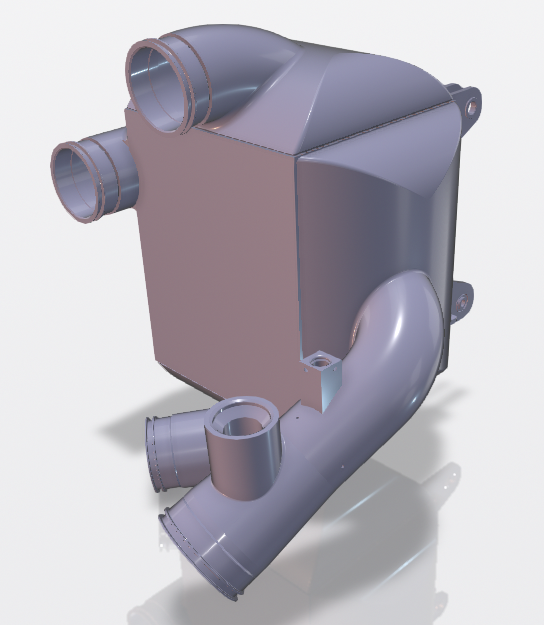
Reheaters are commonly used in aviation environmental control systems (ECS). They provide moisture control and temperature balance by preventing excessive cooling of the air in a secondary heating cycle. They are particularly used in passenger cabins where high comfort and precise temperature regulation are required.